Understanding UK Energy Performance Certificates (EPCs)
Anyone who has bought, sold or rented a house in the last few years will be familiar with Energy Performance Certificates (EPCs). Featured as a coloured graphic at the bottom of the Estate Agents’ particulars, these charts suddenly became more important as energy prices soared. Below, we describe what EPCs are, how they are calculated, their historical background, their advice to homeowners, and their legal requirements.
Check your EPC here:
The UK implemented Energy Performance Certificates (EPC) in 2007. To help homeowners, tenants, and businesses make informed decisions about energy usage and understand a building’s energy efficiency.
EPCs offer vital knowledge about a property’s energy efficiency, provide recommendations for occupiers/owners to reduce energy consumption, and give potential buyers/renters an idea of the home’s running costs. That quaint crumbling cottage might not be so attractive if keeping warm is expensive.
What are Energy Performance Certificates (EPCs)?
Energy Performance Certificates (EPC) are official documents that assess and rate the energy efficiency of a building. These certificates provide information about the energy consumption and carbon emissions associated with the property and recommendations for improving its energy efficiency. EPCs are legally required in the UK when a property is built, sold, or rented — in 2018, Minimum Energy Efficiency Standards (MEES) were introduced for rental properties.
The primary purpose of an EPC is to provide potential buyers or tenants with an insight into the energy efficiency of a property, allowing them to make knowledgeable decisions regarding their energy usage and related costs. Additionally, EPCs help identify areas where improvements can be made to enhance a property’s energy efficiency, benefiting both the environment and the occupants.
EPC Calculation and Rating Methodology
The calculation and rating methodology used in EPCs is based on various factors related to a building’s construction, insulation, heating systems, and energy consumption. Trained assessors, who may be independent or appointed by accredited organisations, carry out assessments to generate EPCs. The assessments involve examining different aspects of the property, such as its size, construction materials, heating systems, insulation levels, and ventilation.
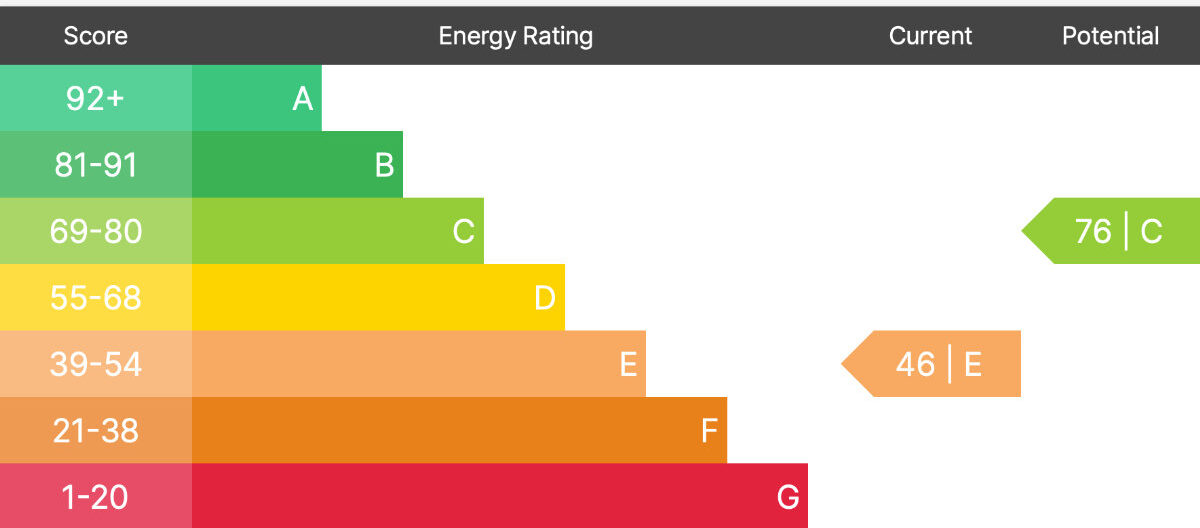
The EPC rating is presented on a scale ranging from A (most efficient) to G (least efficient). Similar to appliance labelling. The rating is determined by calculating the total energy usage per square meter of the property and comparing it to a benchmark figure for comparable buildings. Allowing for a standardised and fair comparison between different properties, regardless of size or type.
The EPC also includes a numerical indicator called the Energy Efficiency Rating, which ranges from 1 to 100. A higher score signifies greater energy efficiency. The EPC report provides a breakdown of the property’s current energy efficiency, potential for improvement, and estimated energy costs.
Historical Backdrop
Energy Performance Certificates were introduced in the UK in 2007 due to the European Union’s Energy Performance of Buildings Directive, which aimed to improve energy efficiency and reduce carbon emissions in buildings across Europe. The UK government implemented the directive through the Energy Performance of Buildings (Certificates and Inspections) (England and Wales) Regulations 2007.
Since their introduction, EPCs have become an integral part of the property market in the UK. They serve as a tool to increase understanding about energy consumption, promote energy efficiency, and help achieve national and international environmental goals.
Advice for Homeowners to Reduce Energy Usage
One of the critical benefits of EPCs is the advice they provide to homeowners on reducing energy consumption and improving their properties energy efficiency. This guidance is handy for those looking to lower their energy bills, minimise their environmental impact, and create a more comfortable living space. The recommendations offered in EPC reports are tailored to each specific property, considering its unique characteristics and current energy performance.
EPCs guidance typically covers a range of areas, including:
Insulation Improvements — the fabric of the building
EPCs often recommend insulation improvements to enhance a property’s energy efficiency. This may involve adding or upgrading insulation in walls, roofs, and floors to reduce heat loss and retain warmth within the building. Proper insulation can significantly reduce the need for excessive heating, resulting in energy savings and increased comfort.
Heating Systems — controls and upgrades
Efficient heating systems play a vital role in reducing energy consumption. EPCs offer advice on upgrading or optimising heating systems, including installing energy-efficient boilers, smart thermostats, and programmable controls. These measures help regulate temperature and reduce energy wastage, lowering energy bills.
The EPC rating considers the cost of heating and powering the dwelling, favouring gas heating due to historically lower gas prices. As a result, EPCs commonly suggest new gas boilers over low-carbon heat pumps. However, recent increases in energy prices have narrowed the gap between gas and electricity prices, making heat pump running costs comparable to gas boilers for many homes. Despite this, the EPC rating system has not yet reflected this change. The government has an action plan to improve EPC calculations, but until then, replacing a gas boiler with a heat pump may reduce the EPC score.
Lighting and Appliances — low-cost, simple recommendations
The choice of lighting and household appliances can considerably impact energy usage. EPCs often recommend switching to energy-efficient lighting solutions, such as LED bulbs, which consume significantly less electricity while providing the same brightness level.

Currently, EPCs do not include appliances as they are not part of the fabric of the building. Even though replacing old and inefficient appliances with energy-saving models will result in substantial energy and cost savings over time.
Renewable Energy Sources — long-term investments
EPC reports may suggest installing renewable energy technologies, such as solar PV panels and wind turbines, to generate clean energy on-site. These renewable sources can supplement or replace traditional energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions and energy bills.
Legal Requirements for Sellers and Landlords
EPCs have been a legal requirement in the UK since 2008 for all domestic and non-domestic properties, whether new or existing, that are sold, rented, or newly constructed. The Energy Performance of Buildings (Certificates and Inspections) (England and Wales) Regulations 2007, later amended in 2012 and 2013, outline the specific legal obligations related to EPCs.
The law requires property owners, including homeowners and landlords, to obtain an EPC before marketing a property for sale or rent. The certificate must be made available to potential buyers or tenants, allowing them to assess the property’s energy performance and associated costs. Failure to comply with these legal conditions can result in penalties and financial consequences.
Minimum Energy Efficiency Standards (MEES) Requirements for Rental Properties
Since 2018, the Minimum Energy Efficiency Standards (MEES) have been in effect in England and Wales, requiring rental properties to have an Energy Performance Certificate (EPC) rating of A to E for legal renting. MEES was introduced in 2015 and made it illegal for landlords to rent properties with an EPC rating below E, meaning poorly insulated F or G-rated homes couldn’t be offered for rent until their rating improved.
The government plans to strengthen MEES further by 2025, only allowing new rental homes with the highest ratings of A, B, or C. Many landlords are unaware of potential rule changes.
EPCs last for ten years, but if legislative changes are implemented, landlords may need a valid EPC at all times, even with the same tenants.
Landlords can be fined for not having a valid EPC, with proposals to raise the fine to £30,000 by 2025. To prepare for potential changes, landlords should check their property’s current EPC and consider improvements to boost the rating, such as insulation, double-glazed windows, or a new boiler.
In Scotland, all privately rented homes must have an EPC rating between A and E since March 2022, with new tenancies requiring a rating of D or above since April 2022. All rented homes must be rated D or above by 31 March 2025. In Northern Ireland, EPCs are mandatory for property sales or rentals, but no specific minimum standard is required.
The UK government offers financial assistance for energy-efficient improvements, and landlords should check if their local council provides any incentives for such modifications.
Commitment to Reducing Carbon Emissions
The introduction of EPCs as a legal requirement reflects the UK government’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions, promoting energy efficiency, and raising awareness about the environmental impact of buildings. It empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding energy consumption and encourages property owners to invest in energy-saving measures.
EPCs Offer Practical Advice to Homeowners, Landlords and Commercial Tenants.
Energy Performance Certificates (EPCs) serve as essential tools in the UK to assess and rate the energy efficiency of buildings. They provide valuable information about energy consumption, carbon emissions, and potential cost savings. EPCs also offer practical advice to occupiers and owners, helping them make informed decisions on energy-saving measures. With the legal requirement to have an EPC when selling a property, the UK government ensures that energy efficiency remains a priority, promoting sustainability and supporting the transition towards a greener future.